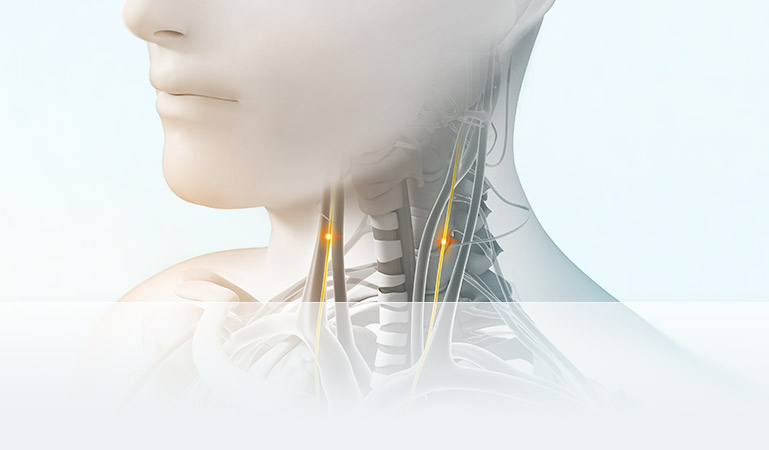
The vagus nerve and nVNS
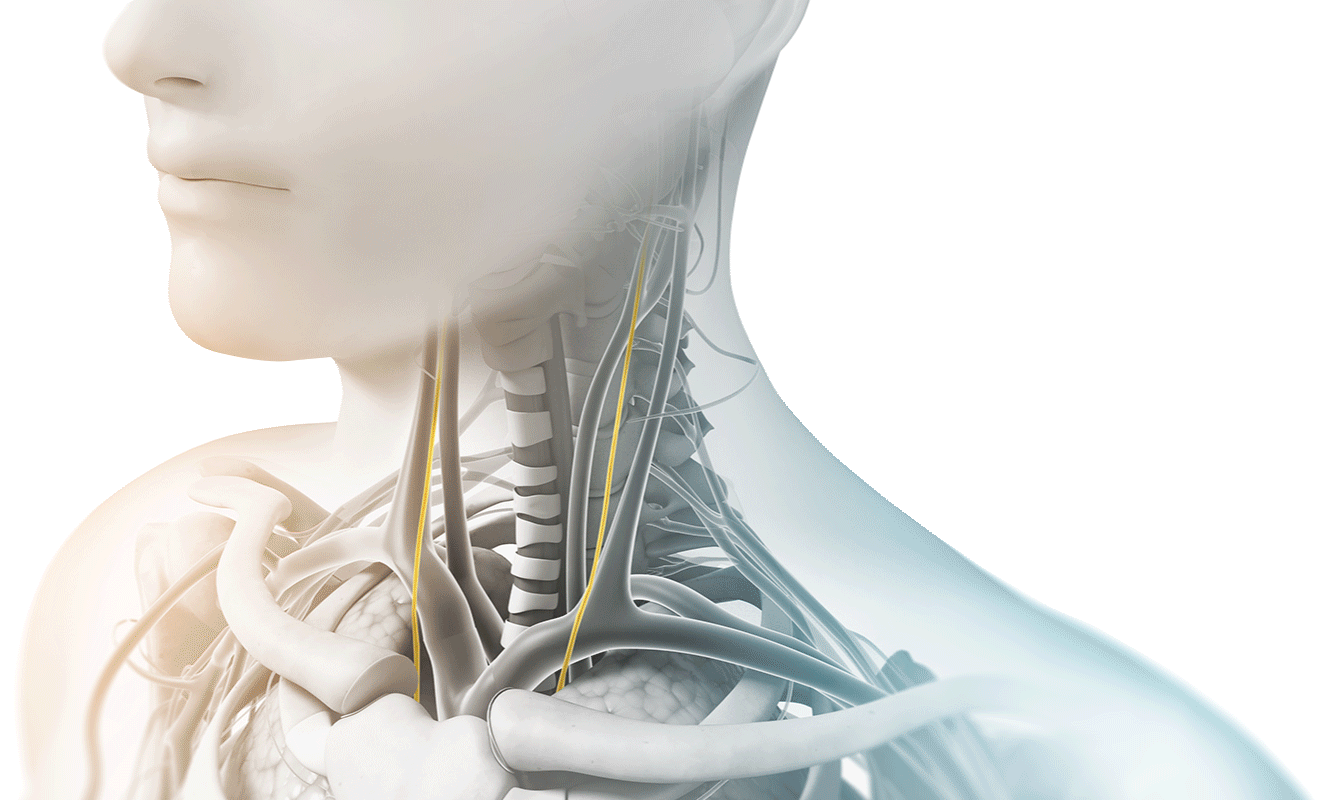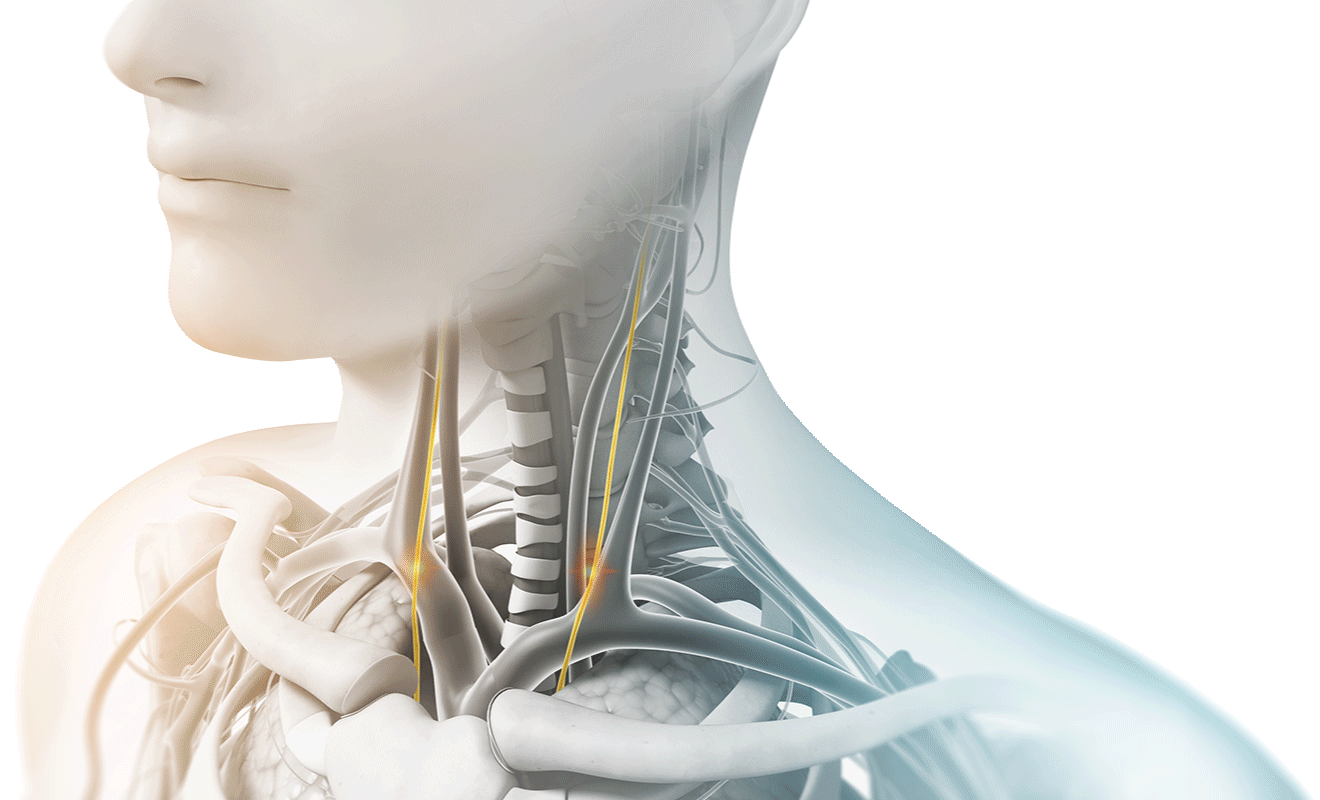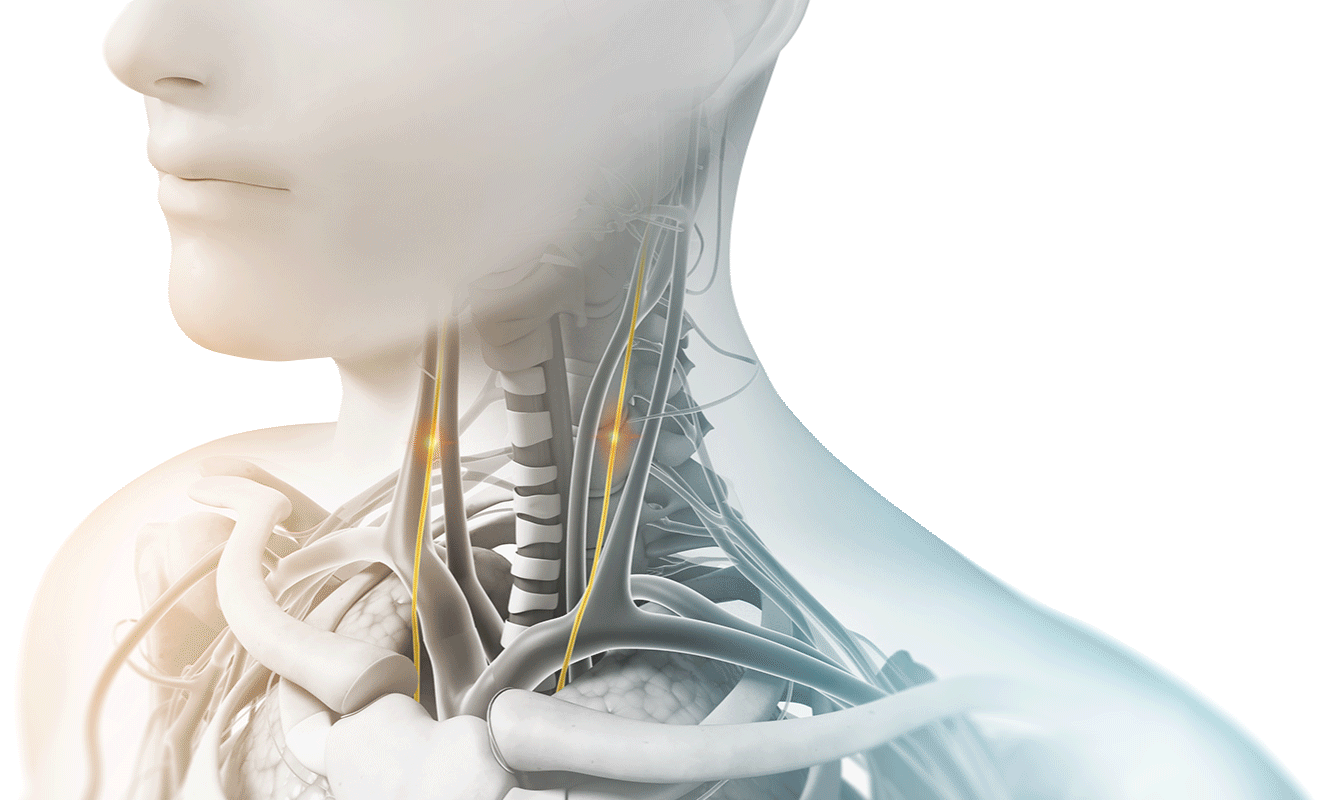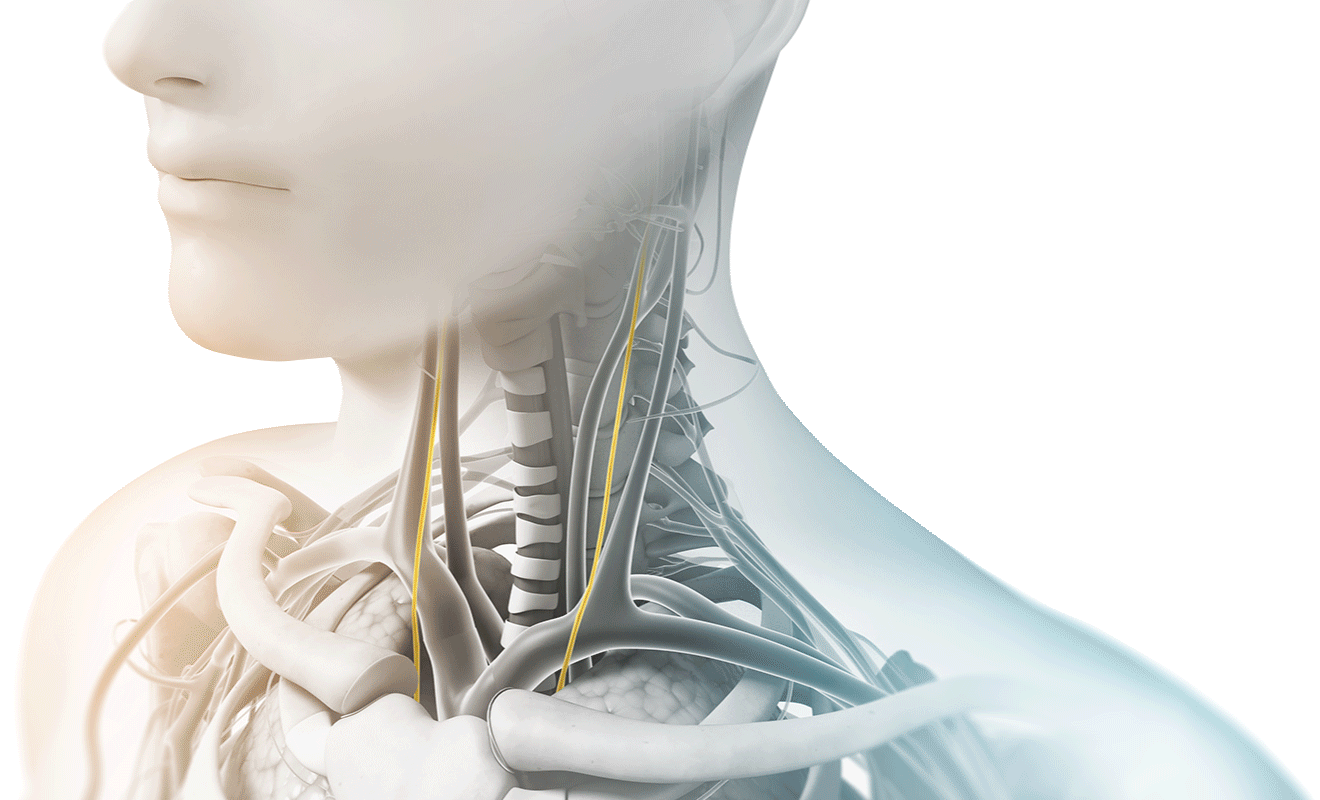
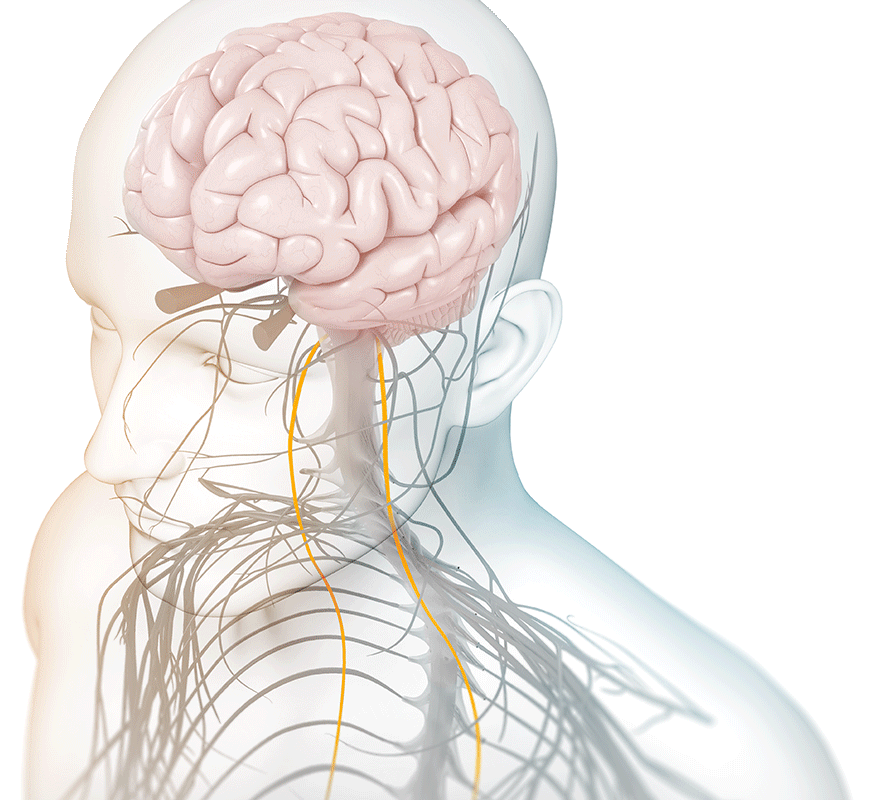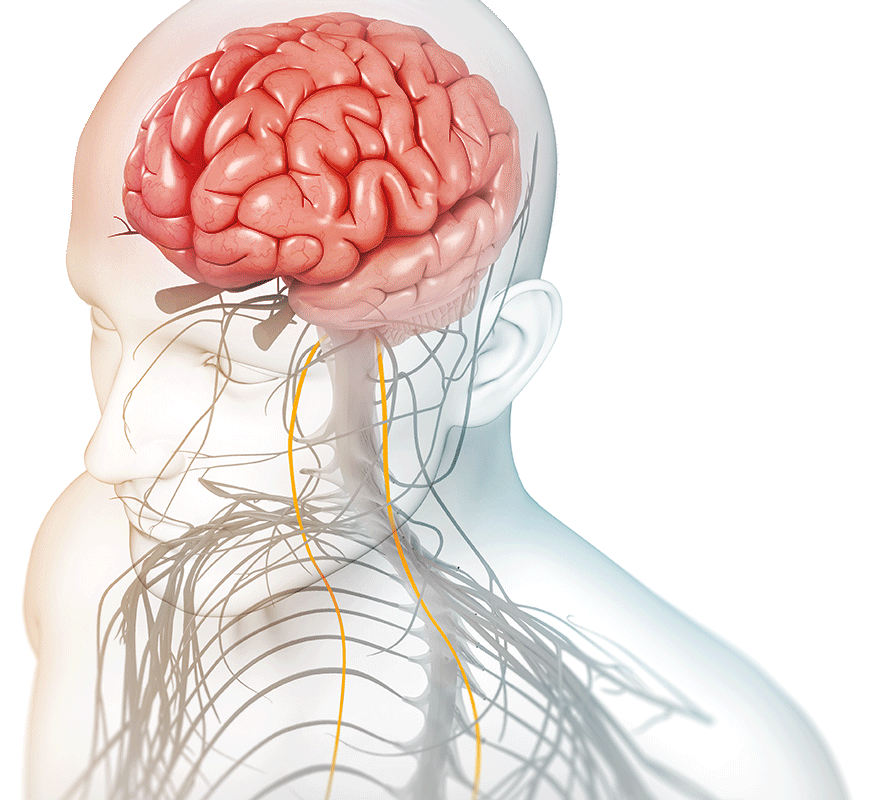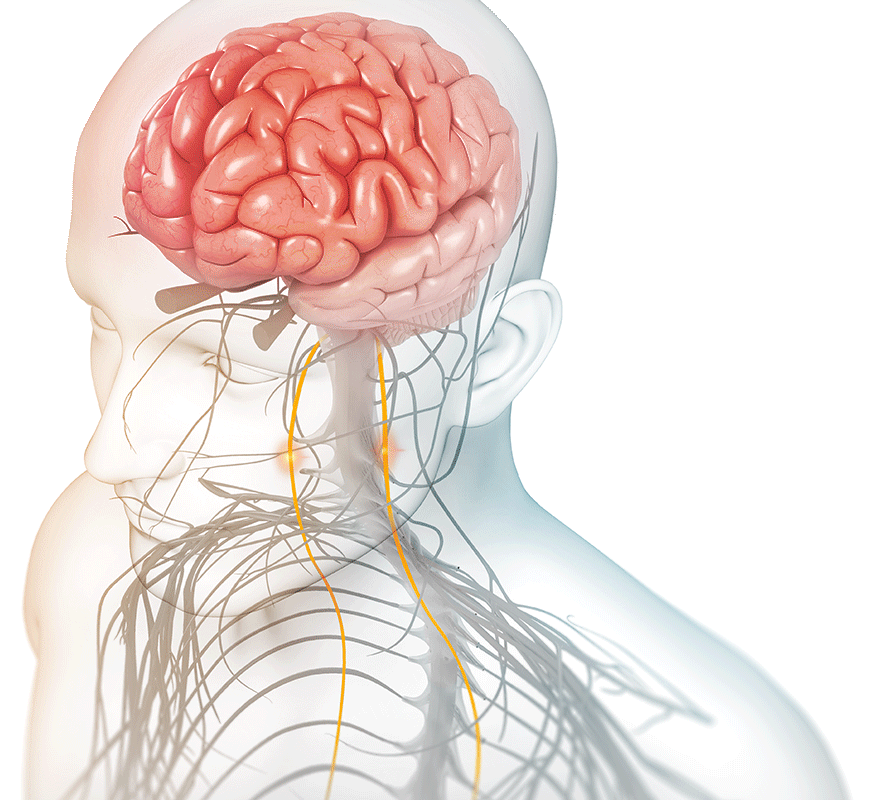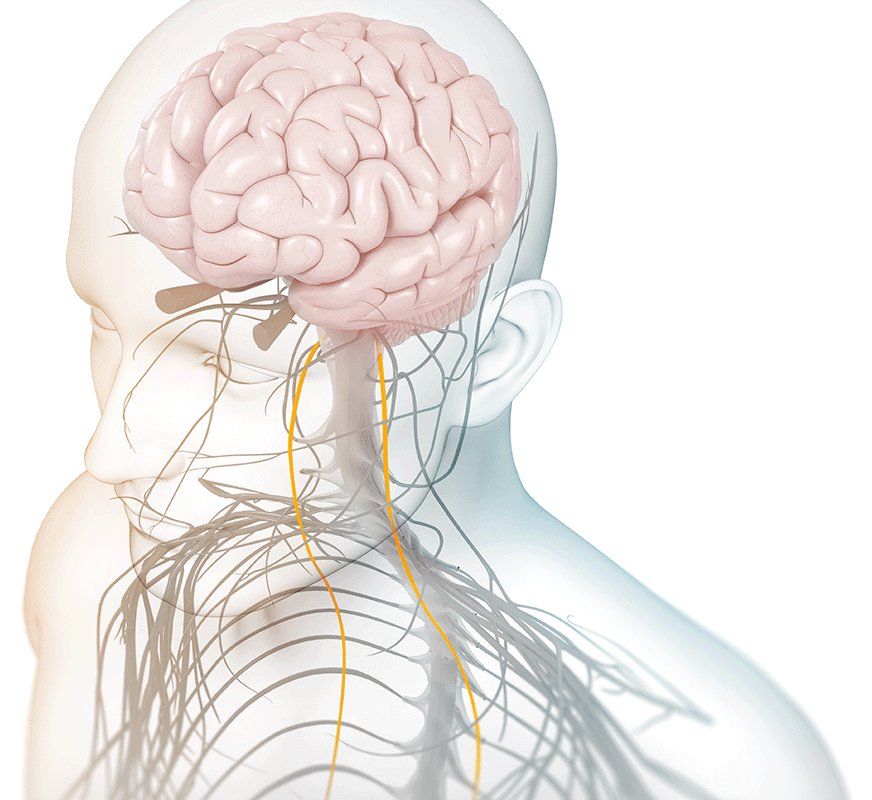
We achieved a technical breakthrough in 2010 when we developed the ability to administer vagus nerve stimulation non-invasively (nVNS) by delivering a proprietary signal through the skin to either the right or the left branches of the vagus nerve in the neck.
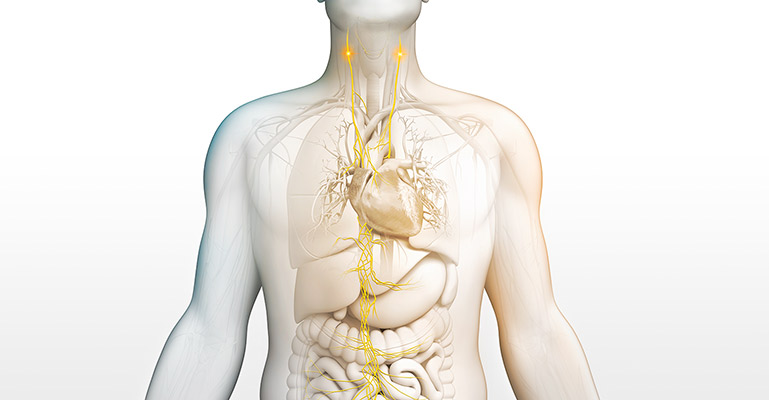
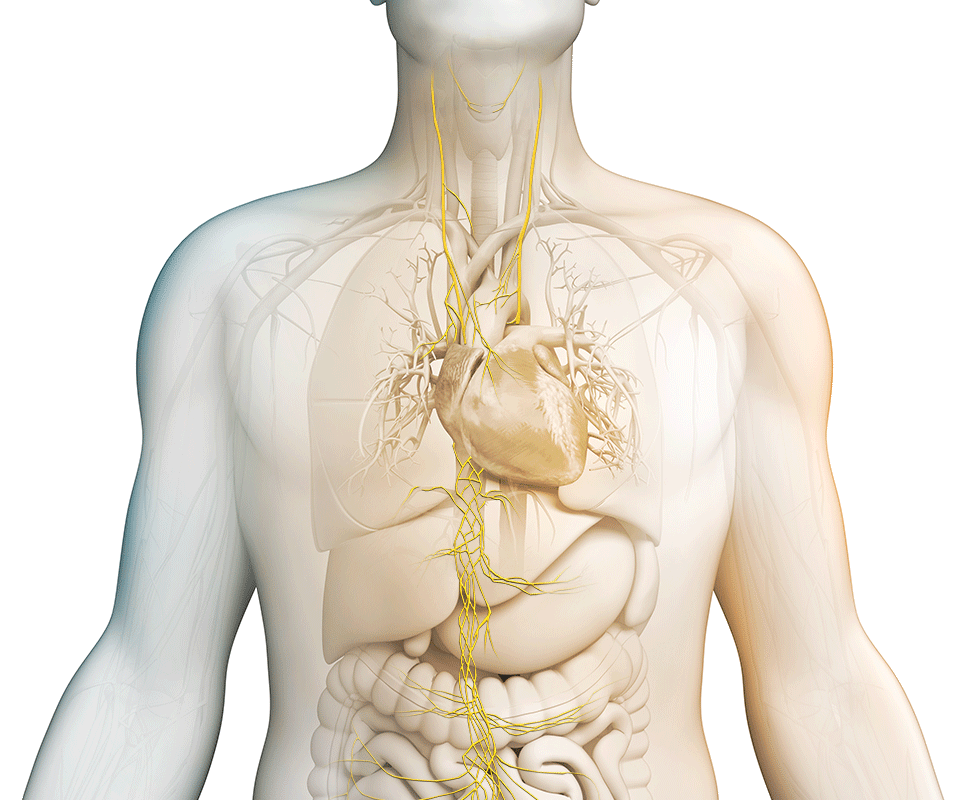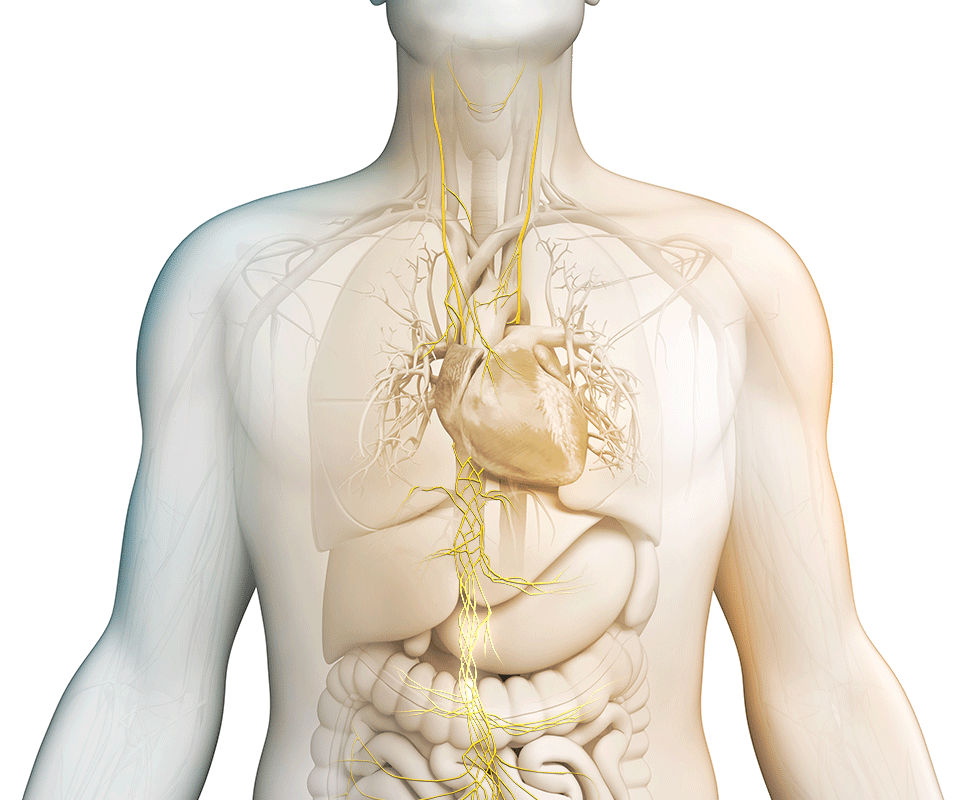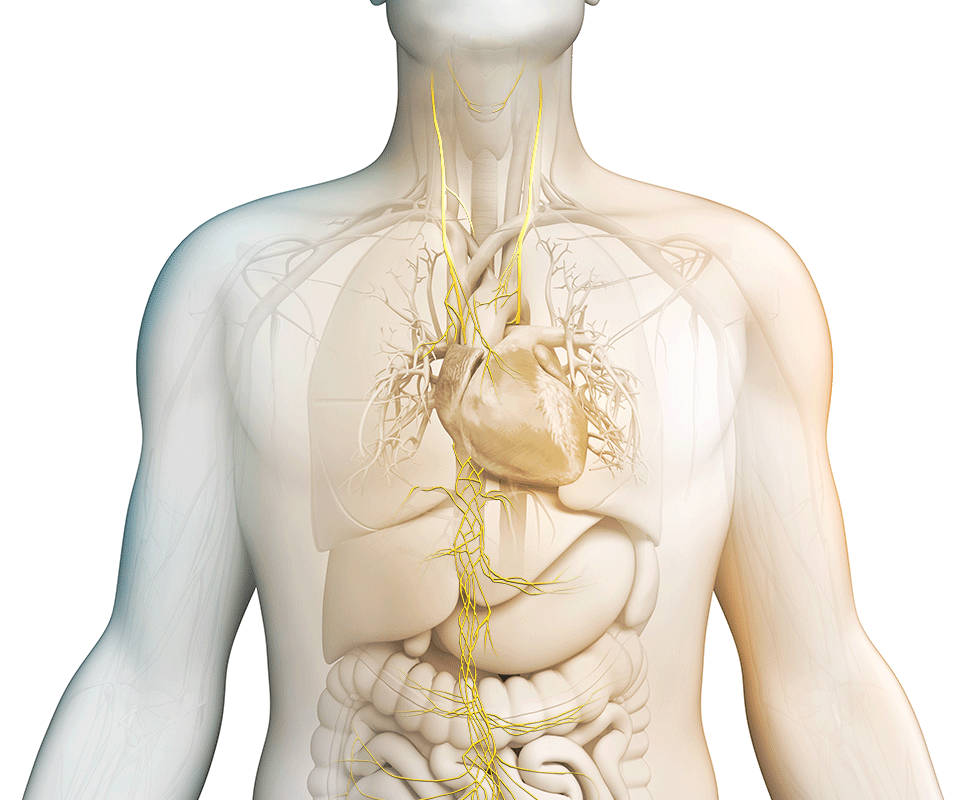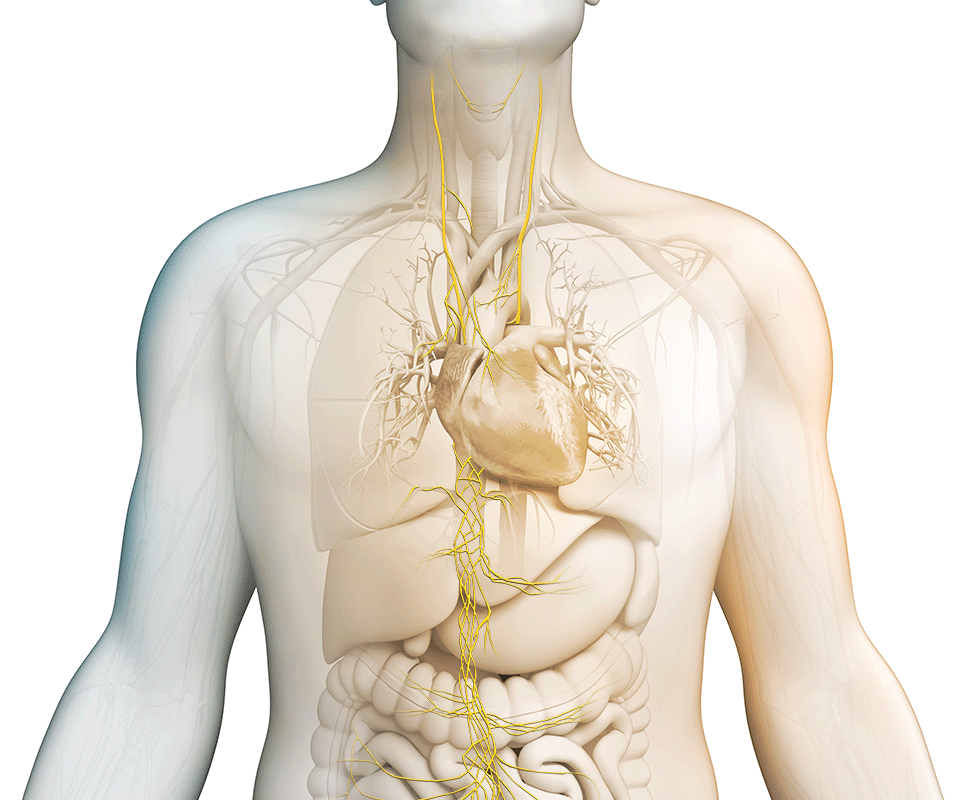
What is the vagus nerve?
It is the longest cranial nerve in the body, primarily serving as a sensory nerve, bringing information from the visceral organs to the brain. The vagus nerve has a number of branching nerves that go to the heart, lungs, voice box, stomach, ears, and other organs. As a sensory nerve that assesses the condition of these organs, it is the communication between the brain and the body. It contains motor and sensory fibers and, because it passes through the neck and thorax to the abdomen, has the widest distribution in the body.
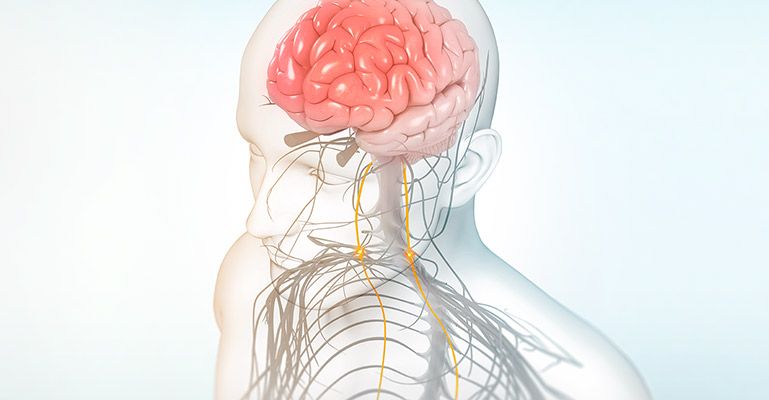
What happens
when nVNS is used?
Stimulating the vagus nerve affects many important autonomic functions in the brain and in the body, including neurotransmitter levels, inflammation levels, and metabolism.


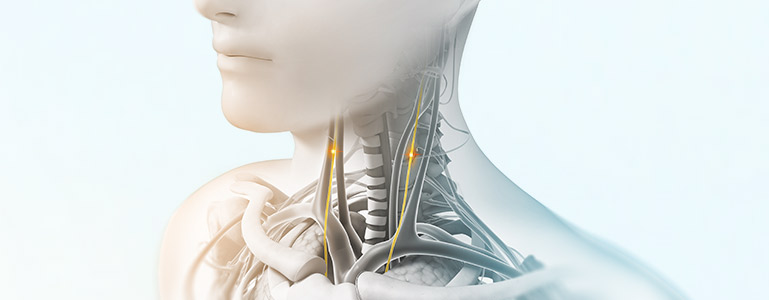
nVNS therapy
Vagus nerve stimulation is a breakthrough technology that helps control multiple disorders.